Abstract
Background Limited data on the relation between quality of life (QoL) and the type of cytoreductive therapy in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) exists.
Methods DALIAH (NCT1387763) was a randomized controlled phase 3 clinical trial. Newly diagnosed patients with MPN ≥ 18 years of age were eligible to enroll. Patients > age 60 were randomized (1:1:1) to receive HU, IFNα-2a, or IFNα-2b and patients ≤ age 60 were randomized (1:1) to receive IFNα-2a or IFNα-2b. HU pre-treatment was allowed from screening and until enrollment.
Symptom burden and overall QoL was measured by the Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Symptom Assessment Form (MPN-SAF) on a scale from 0 (absent/as good as it can be) to 10 (worst-imaginable/as bad as it can be) at baseline, 4, 8, 12, 18, 24, 30, and at data-cutoff at 36 months. Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Fisher's exact test were used for two-group comparisons, and a Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for within-group comparisons. To avoid age-bias the following groups were compared: HU>60 vs IFNα>60 and IFNα-2a vs IFNα-2b. Analyses followed the per-protocol principle.
Results At baseline, the MPN-SAF survey was completed by 199 (98%) of 203 included patients (HU: 38, IFNα-2a/2b>60: 37/37, IFNα-2a/2b≤60: 45/46). Seventy (35%) had ET, 88 (44%) had PV, 16 (8%) had Pre-MF, and 25 (13%) had overt PMF. Median age was 62 years (IQR 50-69) and 113 (55%) were males. Twenty-one (10%) patients had received HU pre-treatment for a median of 19 days (min: 3, max: 44).
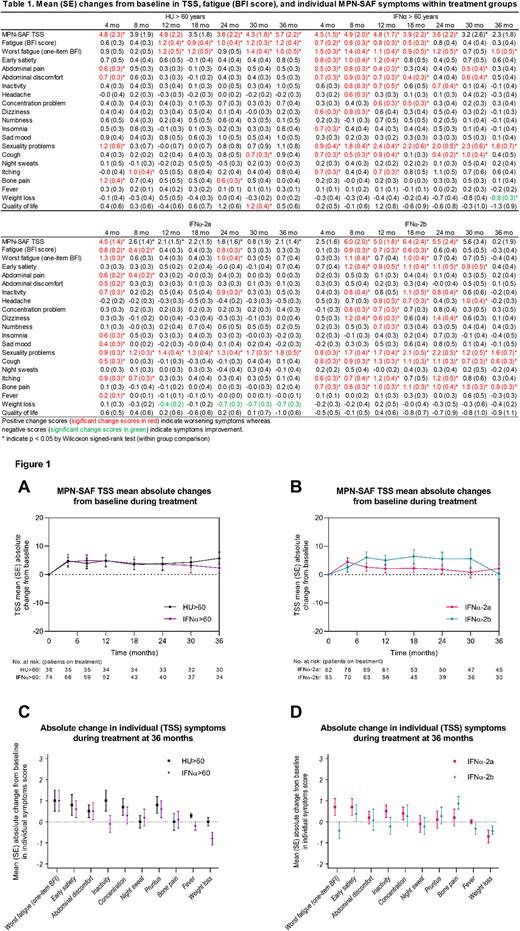
Burden of MPN-symptoms at baseline
Mean Total Symptom Score (TSS, scale 0 [absent]-100 [worst imaginable]) was 15.0 (standard deviation [SD]: 14.3, range 0-69.0). Clinical deficient overall QoL (≥ 4 of 10) was reported in 42% (ET: 46%, PV: 41%, Pre-MF: 38%, PMF: 44%). Fatigue (one-item Brief Fatigue Inventory [BFI]) was the most common symptom (82%) and also carried the highest mean symptom intensity (3.5, SD: 2.8). One or more moderate or severe symptoms (≥ 4 of 10) were reported by 70% of the patients with the most common symptoms (prevalence ≥ 20%) being fatigue (BFI score, 25%) followed by concentration (21%), and insomnia (20%). Severe symptoms (≥ 7 of 10) were reported by 46%. Baseline characteristics as well as TSS and individual symptoms were balanced between groups (HU>60 vs IFNα>60 and IFNα-2a vs IFNα-2b) except abdominal pain, which was higher among IFNα-2b than IFNα-2a, p=0.02.
Burden of MPN-symptoms during treatment
A total of 179 (88%) patients on randomized therapy completed at least one MPN-SAF survey during follow-up, and 96 of 105 (91%) completed the survey at 36 months (HU: 27, IFNα-2a/2b>60: 21/12, IFNα-2a/2b≤60: 22/14). Overall treatment discontinuation rate at 36 months was 48% (HU: 21%, IFNα-2a/2b>60: 43%/65%, IFNα-2a/2b≤60: 47%/63%).
On HU, patients experienced transient or persistent worsening of individual symptoms in fatigue (BFI score), abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, sexuality problems, itching, and bone pain whereas those receiving IFNα (irrespective of age) experienced worsening in fatigue (BFI score), early satiety, abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, inactivity, headache, concentration problems, numbness, dizziness, insomnia, sexuality problems, cough and itching (all, p<0.05). Of note, sad mood and fever was only significantly worsened at 4 months. On IFNα, weight loss was improved (Table 1). TSS increased within the first year in all treatment groups but was only significantly elevated at 36 months compared to baseline among those receiving HU>60 (mean 10.4 to 14.6, p=0.02) (Table 1).
At 36 months, the proportion of patients (baseline TSS>0) achieving a reduction in TSS was similar between groups (HU>60: 23% vs IFNα>60: 30%, p=0.57; IFNα-2a: 33% vs IFNα-2b: 38%, p=0.80), and no significant difference in TSS was observed (HU>60: 14.6 [SD: 13.9] vs IFNα>60: 16.8 [SD: 13.5], p=0.47; IFNα-2a: 17.7 [SD: 13.3] vs IFNα-2b: 15.4 [SD: 15.1], p=0.38) (Table 1, Figure 1A/B). At 36 months, one or more moderate or severe symptoms were reported by 63%. Fatigue (one-item BFI) remained the most common symptom across groups and no significant differences in individual symptom scores or proportion of moderate or severe symptoms were detected between groups (Figure 1C/D).
Conclusion HU and IFNα increased total symptom burden initially in patients with MPN with no significant difference between HU>60 vs IFNα>60 or IFNα-2a vs IFNα-2b. However, at 36 months only patients on HU had significantly increased TSS.
Disclosures
Hansen:Alexion: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; EUSA Pharma: Other: Conference Fee. Larsen:Genentech: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Hasselbalch:Novartis: Consultancy, Other: Grants; AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: Data monitoring board.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Pegylated interferon-alpha-2a (Pegasys) Pegylated interferon-alpha-2b (PegIntron)
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal